NMC2013 HW 1: Difference between revisions
Appearance
No edit summary |
m moved PID2013 HW 1 to NMC2013 HW 1 |
||
| (6 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<font size=5> | <font size=5>PART 1: Buttons vs. Handles</font> | ||
by Bill Verplank | |||
* One way to distinguish the ways we DO things is with HANDLES or BUTTONS. | * One way to distinguish the ways we DO things is with HANDLES or BUTTONS. | ||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
** Make it clear how the user interacts with it. Where are the user's hands? | ** Make it clear how the user interacts with it. Where are the user's hands? | ||
<font size=5> | |||
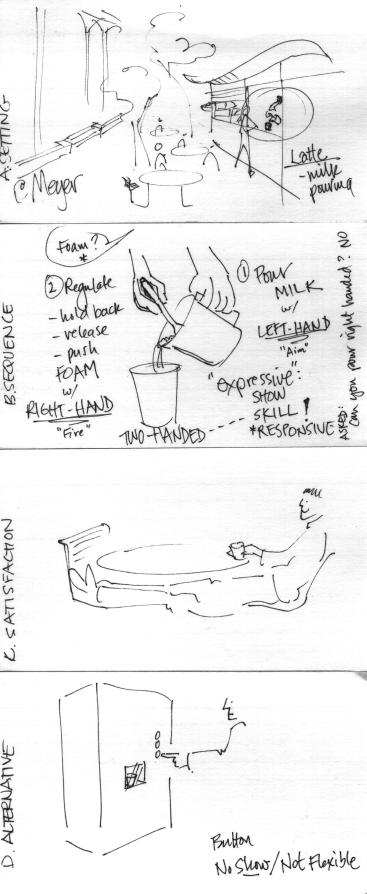
<font size=5>Part 2 - Expressive Scenarios</font><br> | |||
{| | {| | ||
| Line 24: | Line 27: | ||
*Observe someone doing an "expressive" activity. | *Observe someone doing an "expressive" activity. | ||
| Line 37: | Line 39: | ||
*During class | *During class Tuesday morning, we will compare sketches and have a short discussion. In the process, you might have some ideas about a controller that you would like to build for this course. | ||
|- | |- | ||
|} | |} | ||
Latest revision as of 00:22, 29 July 2013
PART 1: Buttons vs. Handles by Bill Verplank
- One way to distinguish the ways we DO things is with HANDLES or BUTTONS.
- Buttons are discrete, handles continuous. With a button you initiate and let go; with a handle you grab on and contol. Button clicks are more likely symbolic - we string them together. Handles are more analogic - we gesture and indicate.
- Bring to class two sketches (8-1/2 x 11); one of a ``handle one of a ``button".
- Sketch enough of the context so it is clear where and who might use it.
- List the features that make this a good or bad example - what you like or don't.
- Tips:
- You will present these to everyone in the class. Use a Sharpie.
- The drawing should be self-explanatory. Use as few words as possible.
- Make it clear how the user interacts with it. Where are the user's hands?
Part 2 - Expressive Scenarios