OSC: Difference between revisions
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
Then you can for example send messages using | Then you can for example send messages using | ||
<pre> | |||
void oscSendMessageInt(char *address, u32 arg) | void oscSendMessageInt(char *address, u32 arg) | ||
void oscSendMessageInt(char *address, u32 arg, u32 arg2) // to send two values at once | void oscSendMessageInt(char *address, u32 arg, u32 arg2) // to send two values at once | ||
</pre> | |||
For example, to sample all eight of the ADC inputs and write them to the OSC address /a2d/1 and /a2d/2, we could use the following code: | |||
<pre> | |||
u08 cnt; | |||
... | |||
oscSendMessageInt(PSTR("/a2d/0"), a2dConvert10bit(0)); // These three lines are inside the main while() loop | |||
oscSendMessageInt(PSTR("/a2d/1"), a2dConvert10bit(1)); | |||
timerPause(10); | |||
</pre> | |||
Revision as of 14:59, 8 October 2008
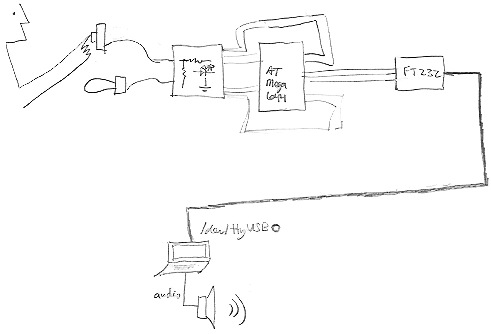
Open Sound Control (OSC) is a networking protocol for real-time musical control information. It was introduced in 1997 by the Center for New Music and Audio Technologies (CNMAT) in Berkeley. It is transport-independent--it can be used over UDP, TDP, WiFi, serial connections, and even within applications. We use it to transfer musical control information from the microcontroller to a computer, which is shown below as a laptop:
The FT232 chip interfaces the microcontroller with a standard Universal Serial Bus (USB) connector. We can use the USB link to open an OSC connection. The microcontroller acts as an OSC client by sending OSC messages. An application running on the computer, such as Pd, acts as an OSC server by receiving and interpreting the OSC messages.
To add OSC functionality to your program
It may be easier to hack one of the examples that uses OSC, but here are the main elements required:
Add $(AVRLIB)/uart.c $(AVRLIB)/ccrma/osc.c $(AVRLIB)/timerx8.c to the SRC line in the makefile so that the compiler knows which additional library source code is needed.
Add the proper includes at the top of the source file.
#include "uart.h" #include "ccrma/osc.h" #include "timerx8.h"
Somewhere early in your program initialize the UART, OSC, the timer, and set the rate at which we communicate over the serial link.
uartInit();
oscInit();
timerInit();
uartSetBaudRate(115200);
Then you can for example send messages using
void oscSendMessageInt(char *address, u32 arg) void oscSendMessageInt(char *address, u32 arg, u32 arg2) // to send two values at once
For example, to sample all eight of the ADC inputs and write them to the OSC address /a2d/1 and /a2d/2, we could use the following code:
u08 cnt;
...
oscSendMessageInt(PSTR("/a2d/0"), a2dConvert10bit(0)); // These three lines are inside the main while() loop
oscSendMessageInt(PSTR("/a2d/1"), a2dConvert10bit(1));
timerPause(10);