Soundcaster: Difference between revisions
Appearance
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 46: | Line 46: | ||
[http://www.idmil.org/projects/the_t-stick T-Stick - IDMIL] | [http://www.idmil.org/projects/the_t-stick T-Stick - IDMIL] | ||
[https://ccrma.stanford.edu/~woony/works/brbi/ BRBI] | [https://ccrma.stanford.edu/~woony/works/brbi/ BRBI - Woon Seung Yeo] | ||
[http://www.icst.net/fileadmin/data/pdf/js/NIME2013_Quarterstaff.pdf Quarterstaff - Jan Schacher] | [http://www.icst.net/fileadmin/data/pdf/js/NIME2013_Quarterstaff.pdf Quarterstaff - Jan Schacher] | ||
Revision as of 06:39, 4 November 2013
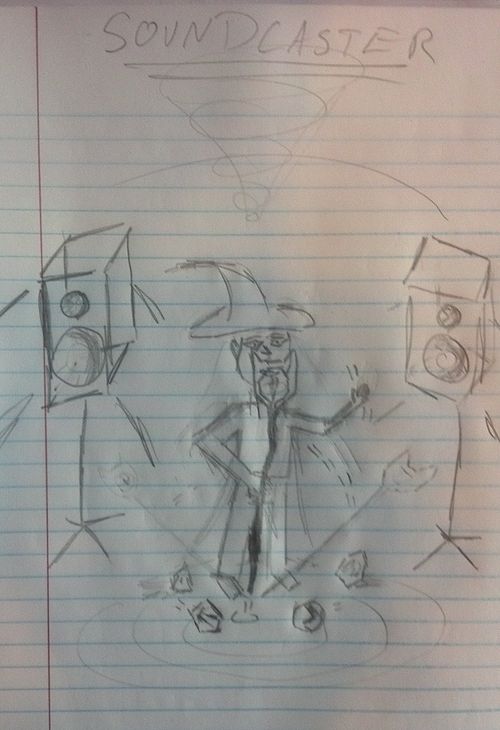
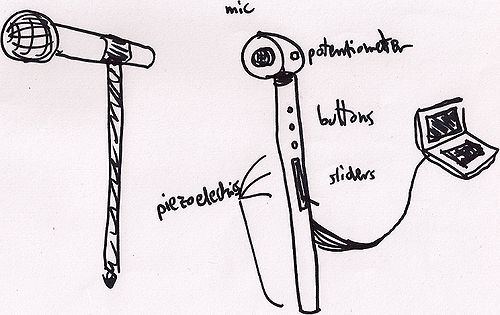
Name: SoundCaster
NEED:
1. Mic
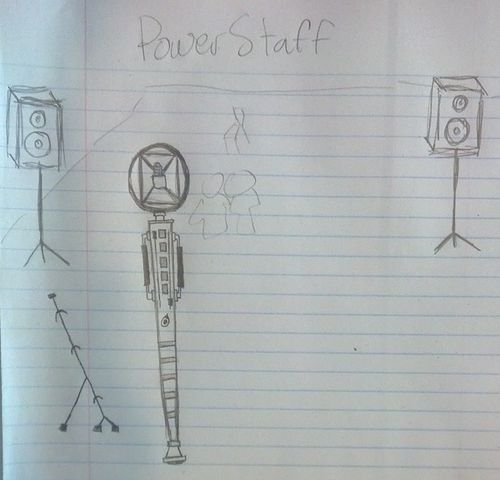
2. Staff
- Accelerometer
- Measure tilt angle, which then can be mapped to quantized region in space -> speaker fader
- wood (plastic for prototype?)
3. Panning
- Stereo setup
WANT:
1. Looper
- Voice sample effects: reversal, amplitude modulation, formant filtering...
2. Sound spatialization
- Sample selection and spatial control
- Spatial quantization for region mapping to speakers
3. Buttons for control selection
4. Stomp for effects (massive reverb for instance) - piezo?
- Rubber cap at bottom of staff
5. Gyroscope
NICE TO HAVE:
1. Hand gestures for extra effects (i.e. distortion, extremely gestural distance control) 2. Accelerometer tornado effects 3. More speakers 4. Pressure sensors / soft pots - used in conjunction with original pitch to pitch shift
STEPS:
1. Get mic (build or buy) 2. Makeshift staff (i.e. 2x4, PVC pipe, broom handle, etc.) 3. Tinker with sensors duct-taped to staff to achieve sound design 4. Create sound design (PD): sample and pan
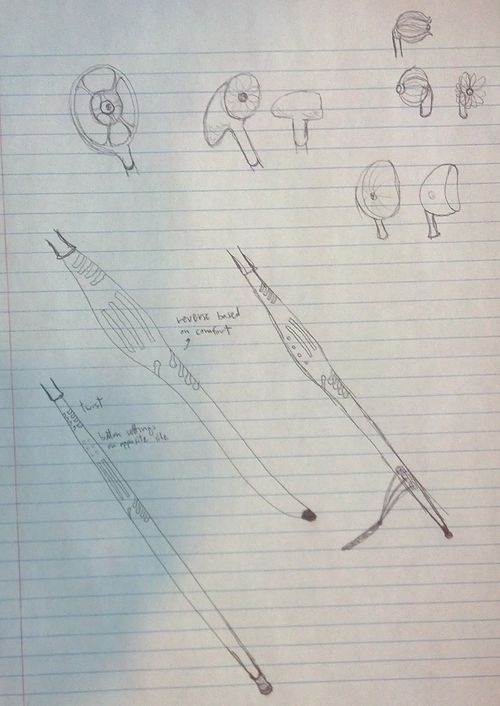
PROJECT SKETCHES
References: